

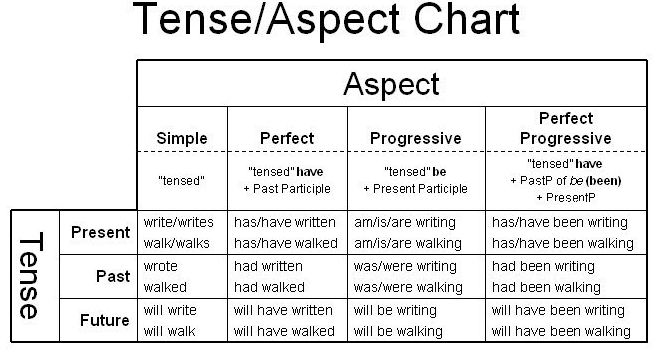
Here, the verb “be” appears in the past tense “was.” And “stolen” is the past participle of “steal.” In English, the most basic passive voice is formed with be + past participle. We can use passive voice when we do not know who or what performed the action or when identifying the performer is not important. You could say, “My bike was stolen.” There is no mention of the person because you do not know who did it. Take the example "You called a friend." The subject is "You” and the subject performs the action “called.”īut sometimes the subject is acted upon or receives the action of the verb. In most sentences in English, the subject performs the action of the verb. Next, let’s talk about the passive voice – the second use for the past participle. Simply note that they are perfect tenses and perfect tenses use past participles.Īn engineer rides his specially-designed bicycle near Agartala, India with his daughter. The speaker used the past participle “studied” as part of the past perfect verb “had studied.”Īgain, do not worry if you do not know the names of these verb tenses. She had studied English before moving to the U.S. The thing to remember is this: All perfect tenses in English include the past participle. Knowing the name of this or other verb tenses is not important for today’s lesson. I used the present perfect tense, which is have or has + past participle. The first we will look at is perfect verb tenses.Īs a reminder, a perfect tense is one that puts some form of the verb “have” before its main verb. OK, now let’s get into today’s subject: the three uses for past participles. Its past tense is “took,” as in “I took my mother to the park.” The past participle is “taken,” as in “She has taken that flight many times.” Most English verbs are regular, so most of their past participles are identical to the past tense.īut for irregular verbs, the past participles and past tenses are not the same. In other words, it is identical, as in “I have talked to her about my plans.” You probably know that the past tense of a regular verb ends in -ed, as in “I talked to my friend.” For regular verbs, the past participle also ends in - ed. The past participle is everywhere so let me begin with a quick discussion about recognizing it. In fact, I used it a few times in this paragraph alone.

You just may not have known what it was called. On today’s program, I will talk about all three of these.īy now in your English studies, you have heard and seen the past participle countless times.

One is the passive voice and the other is adjectives. In addition to forming verb tenses, the past participle can form two other things. Take the statement “I have been to Atlanta.” It uses “been,” which is the past participle of the verb “be.” Most English tenses use a word form called a “participle.” There are present participles and past participles. As you know, English does this through verb tenses.
( thinking = present participle going=gerund, object of the preposition “about”) I’m thinking about going to the concert.It is important to be able to distinguish between a gerund and a present participle in English because often the form of a gerund in another language will differ from that of the present participle. As a noun, the gerund can be a subject, direct or indirect object, or an object of a preposition. The “-ing” form of a verb is called a gerund when it functions as a noun. (“Boarding the bus” is a phrase that describes the passenger.) Example: Boarding the bus, the passenger tripped and fell. Example: The grueling workout exhausted me. Example: I am explaining the use of the present participle. A present participle is a verb in the “-ing” form.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
